Marketing Hotline:
(+86)0532-88988868
(+86)0532-88988868
RO membranes and ultrafiltration membranes are vastly different, and their effects on water treatment are also very different. So, how do we distinguish between them? The best way is to let the data speak.
1. Different working principles
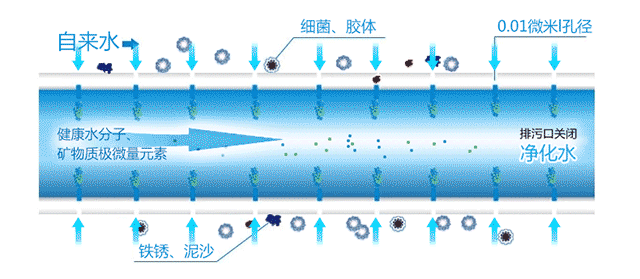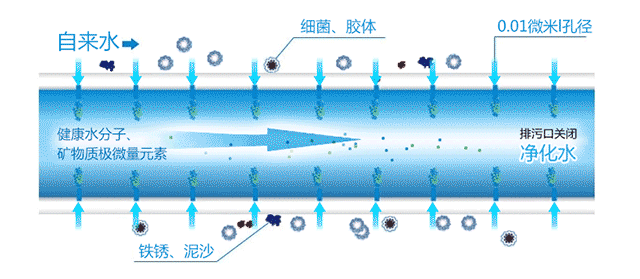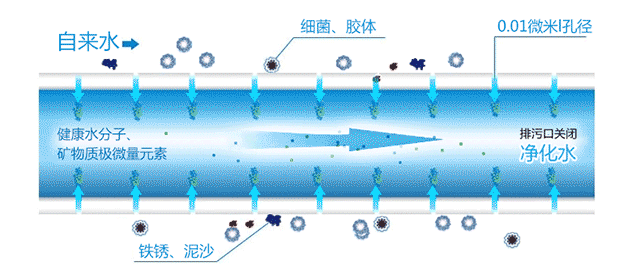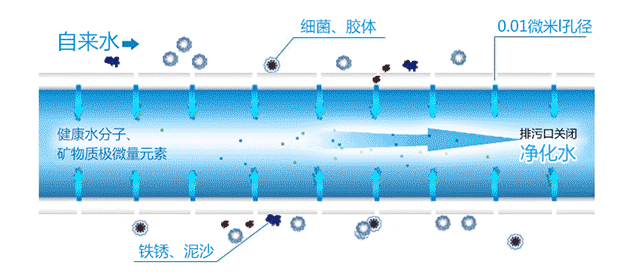
Before we go into detail about RO membranes and ultrafiltration membranes, we must first understand their working principles. When raw water enters the ultrafiltration membrane pipeline, under the influence of the water pressure difference on both sides of the membrane, small molecular beneficial substances can pass through the pores on the membrane surface and be discharged through the outlet, turning into purified water. Unqualified substances, or those with larger molecular weights that cannot pass through, will remain on one side of the membrane. This achieves the purpose of purification, separation, and concentration of the solution. It is suitable for water treatment needs with medium pollution levels and low hardness water sources.
Reverse osmosis technology, also known as RO membrane technology, allows water molecules to pass through the membrane under pressure, while impurities cannot pass through the RO membrane, thereby achieving the separation of pure water and impurities. RO membranes can filter out heavy metals, organic matter, bacteria, residual chlorine, and other substances from water, and since the reverse osmosis membrane does not remove dissolved oxygen, the produced water is living water, making it especially suitable for treating highly polluted and high-hardness water sources.
2. Different filtration accuracy
Ultrafiltration membranes have a filtration precision of 0.01 microns, capable of removing microorganisms, colloids, diatoms, and other substances that cause turbidity. They have good hydrophilicity, long service life, strong anti-fouling ability, and can retain beneficial minerals. They are mainly used in kitchen water purifiers and have a relatively high water output.
Reverse osmosis (RO) membranes have a filtration precision of 0.0001 microns (one ten-thousandth of a micron), making them the highest-precision filter elements currently available. They can filter harmful substances in water such as bacteria, heavy metals, organic compounds, residual chlorine, and colloids. RO membranes provide consistently purified water, have a long service life, automatic drainage, high water output, and ensure safe drinking water.
3. Different Apertures
Ultrafiltration membranes are microporous filtration membranes with uniform pore sizes, with pore sizes ranging from 0.001 to 0.02 microns. When appropriate pressure is applied on one side of the membrane, solute molecules smaller than the pore size can be filtered out, separating particles with a molecular weight greater than 500 Daltons (atomic mass units) and a size larger than 10 nanometers.
The pore size of reverse osmosis (RO) membranes is only 1/100 of that of ultrafiltration membranes, so RO membranes can remove extremely small organic molecular contaminants in water, such as chemical organics and organic pesticide residues, which ultrafiltration membranes cannot. RO membranes also have the effect of softening water, turning hard water into soft water.


